Female Pattern Baldness
Female pattern baldness, also known as female androgenetic alopecia, is a common form of hair loss in women.
If this relates to you, come in for a free hair consultation now! Our hair specialists are sure to help you out!
Understanding
Female Pattern Baldness:
Understanding Female Pattern Baldness is crucial for women facing hair loss concerns. Just like Male Pattern Baldness, Female Pattern Baldness follows a similar hair growth cycle.
While it is less talked about than male pattern baldness, it affects a significant number of women worldwide. Female pattern baldness is characterized by a gradual thinning of hair on the top of the scalp and widening of the part.
Let’s explore the key aspects of this condition and how it affects women’s hair:
What Causes Female Pattern Baldness?
Similar to Male Pattern Baldness, Female Pattern Baldness is influenced by various factors:
Genetics: Family history plays a significant role in Female Pattern Baldness. If there’s a genetic predisposition to hair loss on the maternal or paternal side of the family, women may be more susceptible to this condition.
Hormones and Androgens: Hormones, including androgens, play a vital role in hair growth regulation. In Female Pattern Baldness, androgens, such as DHT, may interact with hair follicles, leading to hair miniaturization and thinning.
Age and Hormonal Changes: Hormonal flunctuations, such as those experienced during menopause, can impact hair follicles’ sensitivity to androgens and contribute to hair thinning and loss.

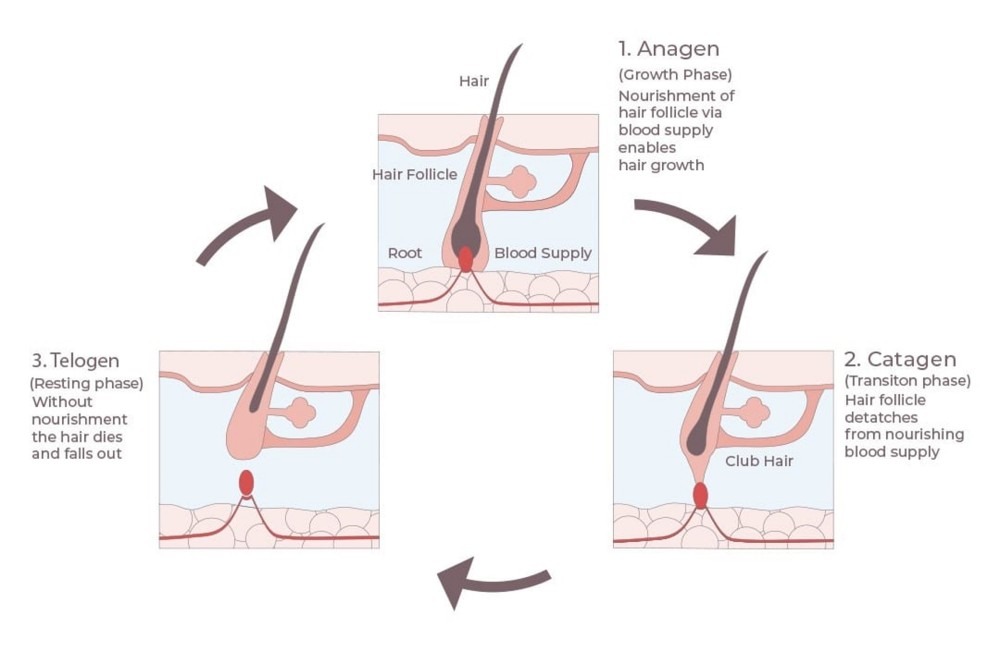
The Hair Growth Cycle:
The hair growth cycle consists of three main phases:
1.Anagen Phase (Growth Phase): This is the active growth phase when hair follicles produce new hair cells rapidly, resulting in visible hair growth. The duration of the anagen phase varies from person to person, affecting hair length and volume.
2.Catagen Phase (Transition Phase): In this transitional phase, hair growth slows down, and hair follicles shrink. The hair detaches from the blood supply, preparing to enter the next phase.
3.Telogen Phase (Resting Phase): The telogen phase is a resting period for the hair follicle. The hair is fully formed but not actively growing. After a few weeks, the hair sheds naturally, and the hair follicle re-enters the anagen phase to start a new hair growth cycle.
How Female Pattern Baldness Affects the Hair Cycle?
Female Pattern Baldness disrupts the hair growth cycle in a similar manner as Male Pattern Baldness:
1.Miniaturization of Hair Follicles: Under the influence of genetic and hormonal factors, hair follicles become more sensitive to androgens like DHT. This leads to gradual hair miniaturization, producing thinner and weaker hairs with each growth cycle.
2.Shortened Anagen Phase: As Female Pattern Baldness progresses, the anagen phase becomes shorter, resulting in shorter hair growth and reduced hair volume.
3.Reduced Hair Density: Thinning and miniaturization of hair follicles lead to decreased hair density, causing areas of visible scalp and overall hair thinning.


Taking Control of Female Pattern Baldness:
Early intervention and personalized treatments are essential for managing Female Pattern Baldness effectively. At DRx Trichology Centre, our experienced trichology specialists offer customized solutions to address hair loss concerns in women. Take the first step towards healthier, fuller hair by scheduling a free consultation today. Let’s begin your hair revitalization journey together!


